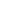Where is Solomon Islands located?
What countries border Solomon Islands?
Solomon Islands Weather
What is the current weather in Solomon Islands?
Solomon Islands Facts and Culture
What is Solomon Islands famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The essence of village life and welfare is the wantok or 'one talk' system. Wantoks, who are people of the... More
- Family: The family unit consists of both parents and their children. The members of the extended family keep close ties. Generally,... More
- Personal Apperance: Dress is casual, with men wearing shorts and T-shirts, and women wearing under-the-knee skirts. Men and women often wear lavalavas... More
- Recreation: Recreational activities commonly found on the Solomon Islands: Diving and Snorkeling: The Solomon Islands are renowned for their stunning coral reefs... More
- Diet: Much of the food is grown in family gardens or wild food from the forest. Staples include cassava, sweet potato,... More
- Food and Recipes: Village breakfast may consist of the leftovers from last night's meal. Tea, coffee, and Milo are used more by urban... More
- Visiting: Visiting is a vital part of life in the Solomon Islands. Formal invitations are only for a feast, although townsfolk... More
- Dating: The wantoks arranged the traditional marriages. The groom's family customarily paid the bride's parents a bride price of shell money,... More
Solomon Islands Facts
What is the capital of Solomon Islands?
| Capital | Honiara |
| Government Type | parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm |
| Currency | Solomon Island Dollar (SBD) |
| Total Area |
11,157 Square Miles 28,896 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Oceania, group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, east of Papua New Guinea |
| Language | Melanesian pidgin in much of the country is lingua franca; English is official but spoken by only 1%-2% of the population. |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $2,000.00 (USD) |
Solomon Islands Demographics
What is the population of Solomon Islands?
| Ethnic Groups | Melanesian 93%, Polynesian 4%, Micronesian 1.5%, European 0.8%, Chinese 0.3%, other 0.4% |
| Languages | While English is the official language, there are 65 indigenous languages spoken in the Solomons. Solomon Island Pijin enables islanders from differing language groups to communicate. The vocabulary is English, but the grammar is Melanesian. 93% are Melanesians, 4% are Polynesian, and some Micronesians re-settled from the Gilbert Islands. |
| Nationality Noun | Solomon Islander(s) |
| Population | 685,097 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.12% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | HONIARA (capital) 68,000 |
| Urban Population | 20.500000 |
Solomon Islands Government
What type of government does Solomon Islands have?
| Suffrage | 21 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Solomon Islands dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 7 July (1978) |
| Constitution |
history: adopted 31 May 1978, effective 7 July 1978; note - in late 2017, provincial leaders agreed to adopt a new federal constitution; progress has been stalled, but as of February 2023, the draft constitution was with the Constitutional Review Unit in the prime minister's office amendments: proposed by the National Parliament; passage of constitutional sections, including those on fundamental rights and freedoms, the legal system, Parliament, alteration of the constitution and the ombudsman, requires three-fourths majority vote by Parliament and assent of the governor general; passage of other amendments requires two-thirds majority vote and assent of the governor general; amended several times, last in 2018 |
| Independence | 7 July 1978 (from the UK) |
Solomon Islands Video
YouTube: Visit Solomon Islands National Geographic - The Solomon Islands
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Solomon Islands Geography
What environmental issues does Solomon Islands have?
| Climate | tropical monsoon; few extremes of temperature and weather |
| Environment - Current Issues | deforestation; soil erosion; many of the surrounding coral reefs are dead or dying |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly rugged mountains with some low coral atolls |
Solomon Islands Economy
How big is the Solomon Islands economy?
| Economic Overview |
The Solomon Islands, a Pacific island nation, has been experiencing economic growth but faces challenges related to infrastructure, governance, and external shocks. Key Economic Indicators: GDP Growth: The Solomon Islands have seen modest economic growth in recent years, driven by sectors such as agriculture, fisheries, forestry, and mining. Tourism and services also contribute to the economy. Agriculture and Fisheries: Agriculture, including subsistence farming and cash crops, plays a significant economic role. The fishing industry is crucial for both domestic consumption and export. Forestry and Logging: The Solomon Islands export timber and logs, contributing to government revenue. However, concerns about sustainable forestry practices and their environmental impact have been raised. Mining: The mining sector, particularly the extraction of minerals like gold and bauxite, has contributed to economic activity and export earnings. Tourism: The tourism industry has growth potential, given the country's natural beauty and cultural attractions. However, limited infrastructure and transport connectivity have affected its development. Challenges and Issues: Infrastructure Deficiency: Limited infrastructure, including transportation and energy, challenges economic development. Improvements in these areas are crucial to support various economic sectors. Governance and Corruption: Governance issues, including concerns about corruption, have been raised. Strengthening governance structures is essential for sustainable economic development and attracting foreign investment. Vulnerability to External Shocks: The Solomon Islands are susceptible to external shocks, including natural disasters (cyclones and earthquakes) and global economic fluctuations. These events can impact critical sectors like agriculture and tourism. Youth Unemployment: Like many developing nations, the Solomon Islands face challenges related to youth unemployment. Creating opportunities for young people and fostering skill development is essential for long-term economic stability. Government Initiatives Development Plans: The government has implemented development plans to foster economic growth, reduce poverty, and address infrastructure challenges. These plans often focus on diversifying the economy. Foreign Aid and Assistance: Foreign aid and assistance, particularly from regional partners and international organizations, support development projects and address economic challenges. Natural Resource Management: Efforts are being made to ensure sustainable management of natural resources, especially in the forestry and fisheries sectors, to balance economic development with environmental conservation. |
| Industries | fish (tuna), mining, timber |
| Currency Name and Code | Solomon Island Dollar (SBD) |
| Export Partners | Japan 21.1%, China 18.9%, South Korea 15.6%, Philippines 10%, Thailand 7.8%, Singapore 4.4% |
| Import Partners | Australia 32.3%, Singapore 20.2%, Fiji 5.1%, New Zealand 5.1%, Papua New Guinea 4% |
Solomon Islands News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Solomon Islands?
Source: Google News
Solomon Islands Travel Information
What makes Solomon Islands a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Solomon Islands form an archipelago in the Southwest Pacific Ocean approximately 1,200 miles northeast of Australia. The capital, Honiara, is located on the Island of Guadalcanal. Solomon Islands is a parliamentary democracy within the British Commonwealth. Tourism facilities are limited, particularly outside Honiara.
Crime
Petty theft is common in some parts of Solomon Islands, so take extra care while walking the streets, going to the market, or going out at night. Guided or group tours are generally safer than traveling alone. Landowners may demand money if you enter their land without permission. Home invasions, burglaries, and violent crime typically increase in the months approaching the Christmas holiday season.Gang-based criminal activity has increased in and around the Burns Creek area in East Honiara and in the Borderline area, which is close to the Japanese WWII memorial. You should not go alone to the Japanese memorial . Use caution when shopping in the central market area as purse and mobile phone snatching is common. Police have established a post at the Market area where you can report crimes.
Yacht-related robberies have increased. The perpetrators—usually armed with knives and clubs—board yachts at night while the occupants are asleep and steal valuables and money. Most criminals are not deterred even when boats are anchored off-shore.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, you may be breaking local law too. Every care should be given when purchasing pharmaceuticals. There are no guarantees that the medicines you purchase in Solomon Islands are genuine.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in another country, you are subject to its laws. U.S. laws don’t apply, and your U.S. passport won’t help you if you do something illegal overseas. Foreign laws, legal systems, and criminal penalties can be vastly different than those in the United States. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Solomon Islands, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. embassy of your arrest. You may also request to have communications from you forwarded to the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Languages
While English is the official language, there are 65 indigenous languages spoken in the Solomons. Solomon Island Pijin enables islanders from differing language groups to communicate. The vocabulary is English, but the grammar is Melanesian. 93% are Melanesians, 4% are Polynesian, and some Micronesians re-settled from the Gilbert Islands.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Hospitals and pharmacies in Solomon Islands are limited to populated areas and religious missions. The nearest reliable medical facilities are in Australia or New Zealand. There is a hyperbaric recompression chamber in Honiara at the In-the-Zone Medical Centre, phone (677) 23485 or (677) 23482; however, medical conditions resulting from diving accidents may require medical evacuation to Australia or New Zealand. Serious medical treatment requiring hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to Australia, New Zealand, or the United States can cost thousands of dollars. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment for health services. If you anticipate the possible need for medical treatment in Australia, obtain entry permission for Australia in advance. Entry permission for Australia can be granted by the Australian High Commission in Honiara but is easier to obtain before you leave the United States (see section above on Entry/Exit Requirements).Malaria occurs throughout the year in most areas of Solomon Islands. We recommend that you seek medical advice on taking prophylaxis against malaria and that you use an insect repellent at all times. Outbreaks of the mosquito-borne illness, dengue fever, occur from time to time. For information on dengue fever, see the World Health Organization Factsheet. Water-borne, food-borne, parasitic, and other infectious diseases (including hepatitis, tuberculosis, filariasis and sexually transmitted infections) are prevalent, with more serious outbreaks occurring from time to time. We encourage you to consider having vaccinations before traveling. We advise you to boil all drinking water or drink bottled water, and avoid ice cubes and raw and undercooked food. Seek medical advice if you have a fever or are suffering from diarrhea.
Safety and Security
Acts of political violence and civil unrest sometimes occur in Solomon Islands and may coincide with Parliamentary sessions and court cases. In November 2011, the election of a new Prime Minister was followed by protests in Honiara that resulted in some injuries and property damage. Civil unrest can also occur at sporting or cultural events that attract large crowds, especially if alcohol is involved.You can obtain up-to-date safety and security information by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll-free within the U.S. and Canada, or by calling a regular toll line, 1-202-501-4444, from other countries. These numbers are available from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Solomon Islands is provided for general reference only and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Traffic in Solomon Islands moves on the left side of the road. Paved roads are found only in and around Honiara. These two-lane paved roads are poorly marked and have many potholes. Roads are not well lit at night. The remaining roads in Solomon Islands are made of coral or gravel or are dirt tracks. Be careful when driving off main roads to avoid trespassing on communal land.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe