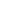Where is Hong Kong located?
What countries border Hong Kong?
Hong Kong Weather
What is the current weather in Hong Kong?
Hong Kong Facts and Culture
What is Hong Kong famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Hong Kong is known as 'The Pearl of the Orient', due to its scenic beauty and the energy of its... More
- Family: With one of the lowest divorce rates in the world, Chinese family loyalty and obedience is extremely strong. One child... More
- Personal Apperance: Modesty and cleanliness is important in the public arena. Hong Kong residents wear a wide range of dress styles, though... More
- Recreation: Hong Kong people do not participate in many sports and do not play them much as kids. More
- Diet: Rice is the staple food. Most of the food in Hong Kong is imported. Fried rice usually includes a little... More
- Food and Recipes: The use of chopsticks is prevalent in Chinese dining. Though Chinese like to share food with the family, work schedules... More
- Visiting: Entertaining visitors is a popular activity in Hong Kong, though due to busy schedules and small homes, dining out in... More
- Dating: Couples enjoy dining out, movies, picnics and shopping malls. Young people usually wait to marry till they can have their... More
Hong Kong Facts
What is the capital of Hong Kong?
| Capital | Victoria |
| Government Type | Presidential limited democracy; a special administrative region of the People's Republic of China |
| Currency | Hong Kong Dollar (HKD) |
| Total Area |
426 Square Miles 1,104 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Asia, bordering the South China Sea and China |
| Language | Chinese (Cantonese), English; both are official |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $57,000.00 (USD) |
Hong Kong Demographics
What is the population of Hong Kong?
| Ethnic Groups | Chinese 95%, other 5% |
| Languages | The official language of Hong Kong is Chinese. English is still the language of commerce, as it was the official language up until 1997. The official dialect is Yue (Cantonese) from Guangdong. Chinese written script has been standardized for centuries, but the simplified script from mainland China is beginning to become popular in Hong Kong. |
| Nationality Noun | Chinese/Hong Konger |
| Population | 7,249,907 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.39% |
| Urban Population | 100.000000 |
Hong Kong Government
What type of government does Hong Kong have?
| Suffrage | 18 years of age in direct elections for 20 of the 90 Legislative Council seats and all of the seats in 18 district councils; universal for permanent residents living in the territory of Hong Kong for the past 7 years; note - in indirect elections, suffrage is limited to about 220,000 members of functional constituencies for the other 70 legislature seats and a 1,500-member election committee for the chief executive drawn from broad sectoral groupings, central government bodies, municipal organizations, and elected Hong Kong officials |
| Citizenship | See China |
| National Holiday | National Day (Anniversary of the Founding of the People's Republic of China), 1 October (1949); note - 1 July (1997) is celebrated as Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Establishment Day |
| Constitution |
History: Several previous (governance documents while under British authority); latest drafted April 1988 to February 1989, approved March 1990, effective 1 July 1997 (Basic Law of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China serves as the constitution); note - since 1990, China's National People's Congress has interpreted specific articles of the Basic Law Amendments: Proposed by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC), the People’s Republic of China State Council, or the Special Administrative Region of Hong Kong; submittal of proposals to the NPC requires two-thirds majority vote by the Legislative Council of Hong Kong, approval by two thirds of Hong Kong’s deputies to the NPC, and approval by the Hong Kong chief executive; final passage requires approval by the NPC |
| Independence | None (special administrative region of China) |
Hong Kong Video
YouTube: ClubTravelie Hong Kong, a Modern Dive into Chinese Culture
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Hong Kong Geography
What environmental issues does Hong Kong have?
| Overview |
The seaward, or south side of Hong Kong Island, is made up of a rugged shoreline with high cliffs and sheltered bays. The interior is rough terrain with steep hills and small valleys. The highest area, known as the Peak, is 555 meters (1,830 ft.) above sea level and has a breathtaking view of the scenic harbor and Kowloon on one side and the offshore islands and South China Sea on the other. The Kowloon Peninsula is directly across the harbor from Hong Kong Island. It is separated from the New Territories by groups of hills, the highest of which rises to more than 3,000 feet. The Kowloon area, with its major subdivisions of Mong Kok and Tsim Sha Tsui, is the leading industrial area of Hong Kong, as well as a major residential area and tourist center with many hotels and shops. The major railway station, Hung Hom, serving Guangzhou, is also located in this densely populated area. The New Territories comprises an area of 355 square miles between Kowloon and the Chinese border and also includes some 235 small offshore islands. This area accounts for most of the HKSAR's agricultural activity and a growing portion of its industrial and residential sectors. The topography is mostly steep hills and marshes, but many places are used for small farms. The only major agriculture on the offshore islands is on Lantau Island, the largest. The remaining islands are small, and, if inhabited, are primarily fishing bases. The rustic character of the New Territories has been transformed in recent years with the construction of major satellite towns such as Sha Tin and Tuen Mun, where large numbers of Hong Kong residents live. |
| Climate | The area's varied climate is governed by the monsoons. Although Hong Kong lies within the Tropics, it enjoys a variety of weather because of these seasonal winds. The winter monsoon blows from the north or northeast from September to mid-March, and the summer wind blows from the south or southwest from mid-March to September. During the summer monsoon, the weather is hot and humid; during the winter monsoon it is cool. Average temperatures range from 58°F in February (with lows in the 40's) to 82°F in July (with highs in the 90's.) The mean relative humidity ranges from a low of 67% in November to 84% in May; many days the humidity approaches 100%, accompanied by heavy clouds. Late fall is the most pleasant time of year, generally with dry and sunny weather and high temperatures of 70° to 75°F. The average annual rainfall is 95 inches. |
| Border Countries | Regional border: China 30 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Air and water pollution from rapid urbanization |
| Environment - International Agreements | Party to: Marine Dumping (associate member), Ship Pollution (associate member) |
| Terrain | Hilly to mountainous with steep slopes; lowlands in north |
Hong Kong Economy
How big is the Hong Kong economy?
| Economic Overview |
Hong Kong has a free market economy, highly dependent on international trade and finance - the value of goods and services trade, including the sizable share of reexports, is about four times GDP. Hong Kong has no tariffs on imported goods, and it levies excise duties on only four commodities, whether imported or produced locally: hard alcohol, tobacco, oil, and methyl alcohol. There are no quotas or dumping laws. Hong Kong continues to link its currency closely to the US dollar, maintaining an arrangement established in 1983. Excess liquidity, low interest rates and a tight housing supply have caused Hong Kong property prices to rise rapidly. The lower and middle-income segments of the population increasingly find housing unaffordable. Hong Kong's open economy has left it exposed to the global economic situation. Its continued reliance on foreign trade and investment makes it vulnerable to renewed global financial market volatility or a slowdown in the global economy. Mainland China has long been Hong Kong's largest trading partner, accounting for about half of Hong Kong's total trade by value. Hong Kong's natural resources are limited, and food and raw materials must be imported. As a result of China's easing of travel restrictions, the number of mainland tourists to the territory surged from 4.5 million in 2001 to 47.3 million in 2014, outnumbering visitors from all other countries combined. After peaking in 2014, overall tourist arrivals dropped 2.5% in 2015 and 4.5% in 2016. The tourism sector rebounded in 2017, with visitor arrivals rising 3.2% to 58.47 million. Travelers from Mainland China totaled 44.45 million, accounting for 76% of the total. The Hong Kong Government is promoting the Special Administrative Region (SAR) as the preferred business hub for renminbi (RMB) internationalization. Hong Kong residents are allowed to establish RMB-denominated savings accounts, RMB-denominated corporate and Chinese government bonds have been issued in Hong Kong, RMB trade settlement is allowed, and investment schemes such as the Renminbi Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor (RQFII) Program was first launched in Hong Kong. Offshore RMB activities experienced a setback, however, after the People’s Bank of China changed the way it set the central parity rate in August 2015. RMB deposits in Hong Kong fell from 1.0 trillion RMB at the end of 2014 to 559 billion RMB at the end of 2017, while RMB trade settlement handled by banks in Hong Kong also shrank from 6.8 trillion RMB in 2015 to 3.9 trillion RMB in 2017. Hong Kong has also established itself as the premier stock market for Chinese firms seeking to list abroad. In 2015, mainland Chinese companies constituted about 50% of the firms listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and accounted for about 66% of the exchange's market capitalization. During the past decade, as Hong Kong's manufacturing industry moved to the mainland, its service industry has grown rapidly. In 2014, Hong Kong and China signed a new agreement on achieving basic liberalization of trade in services in Guangdong Province under the Closer Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), adopted in 2003 to forge closer ties between Hong Kong and the mainland. The new measures, which took effect in March 2015, cover a negative list and a most-favored treatment provision. On the basis of the Guangdong Agreement, the Agreement on Trade in Services signed in November 2015 further enhanced liberalization, including extending the implementation of the majority of Guangdong pilot liberalization measures to the whole Mainland, reducing the restrictive measures in the negative list, and adding measures in the positive lists for cross-border services as well as cultural and telecommunications services. In June 2017, the Investment Agreement and the Agreement on Economic and Technical Cooperation (Ecotech Agreement) were signed under the framework of CEPA. Hong Kong’s economic integration with the mainland continues to be most evident in the banking and finance sector. Initiatives like the Hong Kong-Shanghai Stock Connect, the Hong Kong- Shenzhen Stock Connect the Mutual Recognition of Funds, and the Bond Connect scheme are all important steps towards opening up the Mainland’s capital markets and have reinforced Hong Kong’s role as China’s leading offshore RMB market. Additional connect schemes such as ETF Connect (for exchange-traded fund products) are also under exploration by Hong Kong authorities. In 2017, Chief Executive Carrie LAM announced plans to increase government spending on research and development, education, and technological innovation with the aim of spurring continued economic growth through greater sector diversification. |
| Industries | Textiles, clothing, tourism, banking, shipping, electronics, plastics, toys, watches, clocks |
| Currency Name and Code | Hong Kong Dollar (HKD) |
| Export Partners | China 39.3%, US 21.4%, Japan 5.4% |
| Import Partners | China 44.2%, Japan 11.3%, Taiwan 7.2%, US 5.7%, South Korea 4.7%, Singapore 4.7% |
Hong Kong News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Hong Kong?
Source: Google News
Hong Kong Travel Information
What makes Hong Kong a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Hong Kong, a Special Administrative Region (SAR) of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) since July 1, 1997, has a high degree of autonomy, except in the areas of defense and foreign policy, and retains its own currency, laws, and border controls. It is composed of three geographic areas: the New Territories, Kowloon Peninsula, and Hong Kong Island. Hong Kong SAR is cosmopolitan and highly developed. Tourist facilities and services are widely available.
Crime
Hong Kong has a low crime rate. Even so, you should exercise caution when in congested areas and pay particular attention to personal belongings while in crowded markets and while traveling on public transportation. Violent crime, though rare, does occur.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Hong Kong, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. In Hong Kong you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. If you are found to be driving under the influence, you could be sent immediately to jail. There are also some things that might be legal in Hong Kong, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Hong Kong, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.If you violate Hong Kong laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession of, use of, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Hong Kong are severe, and if you are convicted, you can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. In Hong Kong, detained U.S. citizens have been surprised that they had been arrested for violations that would not have resulted in arrest in the United States.
Arrest notifications in Hong Kong: If you are arrested in Hong Kong, authorities of Hong Kong are required to notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Consulate General in Hong Kong of your arrest.
Languages
The official language of Hong Kong is Chinese. English is still the language of commerce, as it was the official language up until 1997. The official dialect is Yue (Cantonese) from Guangdong. Chinese written script has been standardized for centuries, but the simplified script from mainland China is beginning to become popular in Hong Kong.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Good medical facilities are available, and there are many Western-trained physicians in Hong Kong. Prescription drugs are widely available, although they may have different names from those in the United States. Hong Kong emergency service response times for police, fire, and ambulances are good.Air pollution is increasingly serious in Hong Kong. Congested vehicle traffic and mainland factories pump out ozone, sulfur, and nitrogen oxides, leading to a visible haze in the atmosphere on most days of the year. Average roadside pollution levels exceed WHO guidelines by 200% and continue to deteriorate, creating health risks for those with allergies, asthma, or cardiac problems.
Hong Kong remains at "Alert" response status for Pandemic Influenza.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Hong Kong, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. About 90 percent of the population in Hong Kong depends on public transport. Taxis, buses, and the mass transit railway (MTR) are readily available, inexpensive, and generally safe. The MTR, an underground railway network, is the most popular mode of public transport, carrying an average of 3.5 million passengers a day.In Hong Kong, traffic moves on the left. During the daytime, traffic congests Hong Kong's urban areas. Each year there are about 14,000 traffic accidents in Hong Kong involving more than 18,000 drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. Speed limits are 50 kilometers per hour (kph) (approximately 31 miles per hour (mph)) in urban areas, 80 kph (approximately 50 mph) on highways, and 110 kph (approximately 68 mph) on expressways unless otherwise marked. The use of seatbelts in vehicles, if they are so equipped, is mandatory both in the front and back seats. The maximum penalty for dangerous driving causing death can be a fine of $50,000 HK ($6,500 US), imprisonment for five years, and disqualification from driving for not fewer than two years on first conviction. If you are a driver involved in a traffic accident, you will be required to undergo alcohol-level testing. If you are found to exceed the prescribed limit of blood alcohol, you may face prosecution under Hong Kong law. The use of hand-held cellular phones while driving in Hong Kong is strictly prohibited. If you breach this law, you may be subject to a maximum fine of $2,000 HK ($260 US). However, you can use “hands-free devices,” such as headphones and speakerphones. Hong Kong law requires that all registered vehicles carry valid third-party liability insurance.
You may be issued a Hong Kong driver’s license without a test if you hold a valid U.S. driver’s license, provided you have resided in the United States at least six months. If you do not plan to stay in Hong Kong for more than 12 months you can drive in Hong Kong on your valid U.S. driver’s license. Visit the Hong Kong Transport Department online for further details.
Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. Also, we suggest that you visit the website of the country’s Hong Kong Tourism Board and the Hong Kong Road Safety Council.