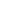Where is Congo, Democratic Republic of the located?
What countries border Congo, Democratic Republic of the?

Congo, Democratic Republic of the Weather
What is the current weather in Congo, Democratic Republic of the?
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Facts and Culture
What is Congo, Democratic Republic of the famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: There exists a general politeness and concern for the welfare of others. This politeness sometimes manifests itself as a gentle... More
- Family: The family is the most important focus in a Congolese life. Although family structure varies greatly between the different ethnic... More
- Personal Apperance: Western-style clothing is common in most urban areas. Congolese women wear a "pagne", a long dress made of a five-yard... More
- Recreation: Soccer is the national sport. People also love to play cards, chess, checkers and board games. Mangual ( a pit... More
- Diet: Common fruits include oranges and coconuts. Common foods include rice, cassava, potatoes, bananas, beans, yams, corn, and other fruits... More
- Food and Recipes: Separate communal bowls are used by men and women at mealtime. Hands are washed before and after each meal. ... More
- Dating: If two young people meet and desire to date, the boy and his family seek permission of the girl's family... More
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Facts
What is the capital of Congo, Democratic Republic of the?
| Capital | Kinshasa |
| Government Type | Semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Congolese francs (CDF) |
| Total Area |
905,350 Square Miles 2,344,858 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Africa, northeast of Angola |
| Language | French (official), Lingala (a lingua franca trade language), Kingwana (a dialect of Kiswahili or Swahili), Kikongo, Tshiluba |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.9% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $800.00 (USD) |
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Demographics
What is the population of Congo, Democratic Republic of the?
| Ethnic Groups | Over 200 African ethnic groups of which the majority are Bantu; the four largest tribes - Mongo, Luba, Kongo (all Bantu), and the Mangbetu-Azande (Hamitic) make up about 45% of the population |
| Languages | Although French is the official language and is used in larger businesses and government, it is spoken by only about 10 percent of the population. Lingala is increasingly used as the national language. Regional languages are: Lingala, Kikongo, Tshiluba, and Swahili. |
| Nationality Noun | Congolese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 101,780,263 |
| Population - note | Note: Estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.54% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | KINSHASA (capital) 8.798 million; Lubumbashi 1.556 million; Mbuji-Mayi 1.504 million; Kananga 888,000; Kisangani 820,000 |
| Urban Population | 34.300000 |
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Government
What type of government does Congo, Democratic Republic of the have?
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal and compulsory |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: no Citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Dual citizenship recognized: no Residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 30 June (1960) |
| Constitution |
History: several previous; latest adopted 13 May 2005, approved by referendum 18-19 December 2005, promulgated 18 February 2006 Amendments: proposed by the president of the republic, by the government, by either house of Parliament, or by public petition; agreement on the substance of a proposed bill requires an absolute majority vote in both houses; passage requires a referendum only if both houses in joint meeting fail to achieve three-fifths majority vote; constitutional articles, including the form of government, universal suffrage, judicial independence, political pluralism, and personal freedoms, cannot be amended; amended 2011 |
| Independence | 30 June 1960 (from Belgium) |
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Video
YouTube: ArconMedia Democratic Republic of the Congo landscapes
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Congo, Democratic Republic of the Geography
What environmental issues does Congo, Democratic Republic of the have?
| Overview | Although the country’s capital, Kinshasa, is only four degrees south of the equator, temperatures are generally moderate. In January, the average daily high is 100 ºF and the low is 80 ºF. In July, the range is from 95 ºF to 75 ºF. The rainy season for Kinshasa and for the two-thirds of the country below the equator lasts from October to May. Despite its dreary sound, the rainy season is not unpleasant. Except for perhaps one rainstorm every few days, lasting anywhere from one to two hours, the skies are usually blue and sunny. In contrast, the dry season, though not yielding any rain, is characterized by overcast and cooler days. |
| Climate |
The Democratic Republic of the Congo straddles the equator in the heart of central Africa and shares a border with nine other countries: the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, and Angola. Congo has access to the Atlantic Ocean on the west through a strip of territory that narrows to 13 miles wide at the coast. Its area includes the greater part of the Congo River Basin and covers 1,465,553 square miles. The Congo River is 2,900 miles long and is the second largest in the world in terms of area drained, flow, and navigable length. With its tributaries, the river provides Congo with about 9,000 miles of navigable waterways, and its force affords Congo 13% of the world's hydroelectric power potential. With the country's abundance of natural resources--which include: copper, cobalt, zinc, industrial and gem-quality diamonds, manganese, tin, crude oil, and gold--Congo is potentially one of the richest countries in the world. The geographical features of this giant African nation are handsome and varied. The huge Congo Basin, a low-lying, bowl-shaped plateau sloping toward the west, is covered by lush, tropical rain forests. Surrounding the basin are mountainous terraces on the west, plateaus merging into savannas to the south and southeast, and dense grasslands toward the northwest. The high picturesque Ruwenzori Mountains bound the basin to the east. |
| Border Countries | Angola 2,511 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of Angola's discontiguous Cabinda Province), Burundi 233 km, Central African Republic 1,577 km, Republic of the Congo 2,410 km, Rwanda 217 km, Sudan 628 km, Tanzania 459 km, Uganda 765 km, Zambia 1,930 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Poaching threatens wildlife populations; water pollution; deforestation; refugees responsible for significant deforestation, soil erosion, and wildlife poaching; mining of minerals (coltan - a mineral used in creating capacitors, diamonds, and gold) causing environmental damage |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands Signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification |
| Terrain | vast central basin is a low-lying plateau; mountains in east |
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Economy
How big is the Congo, Democratic Republic of the economy?
| Economic Overview |
The economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo - a nation endowed with vast natural resource wealth - continues to perform poorly. Systemic corruption since independence in 1960, combined with countrywide instability and intermittent conflict that began in the early-90s, has reduced national output and government revenue, and increased external debt. With the installation of a transitional government in 2003 after peace accords, economic conditions slowly began to improve as the government reopened relations with international financial institutions and international donors, and President KABILA began implementing reforms. Progress on implementing substantive economic reforms remains slow because of political instability, bureaucratic inefficiency, corruption, and patronage, which also dampen international investment prospects. Renewed activity in the mining sector, the source of most export income, boosted Kinshasa's fiscal position and GDP growth until 2015, but low commodity prices have led to slower growth, volatile inflation, currency depreciation, and a growing fiscal deficit. An uncertain legal framework, corruption, and a lack of transparency in government policy are long-term problems for the large mining sector and for the economy as a whole. Much economic activity still occurs in the informal sector and is not reflected in GDP data. Poverty remains widespread in DRC, and the country failed to meet any Millennium Development Goals by 2015. DRC also concluded its program with the IMF in 2015. The price of copper – the DRC’s primary export - plummeted in 2015 and remained at record lows during 2016-17, reducing government revenues, expenditures, and foreign exchange reserves, while inflation reached nearly 50% in mid-2017 – its highest level since the early 2000s. |
| Industries | Mining (copper, cobalt, gold, diamonds, coltan, zinc, tin, tungsten), mineral processing, consumer products (textiles, plastics, footwear, cigarettes), metal products, processed foods and beverages, timber, cement, commercial ship repair |
| Currency Name and Code | Congolese francs (CDF) |
| Export Partners | China 43.5%, Zambia 25%, South Korea 4.9%, Belgium 4.8% |
| Import Partners | China 20.6%, South Africa 17.7%, Zambia 12.3%, Belgium 6.9%, Zimbabwe 5.1%, India 4.7% |
Congo, Democratic Republic of the News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Congo, Democratic Republic of the?
Source: Google News
Congo, Democratic Republic of the Travel Information
What makes Congo, Democratic Republic of the a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (Congo-Kinshasa) (DRC), located in central Africa, is the second largest country on the continent. The capital is Kinshasa. French is the official language. The country endured more than a decade of civil war that ended in 2003, but still faces continuing political instability and extreme poverty.
Crime
In the DRC, poor economic conditions continue to foster crime, especially in urban areas. Most reported criminal incidents in Kinshasa involve crimes of opportunity, which include pick-pocketing and petty theft, often committed by homeless street children called “sheggehs.” Travel in certain areas of Kinshasa, Kisangani, Lubumbashi, and other major cities is generally safe during daylight hours, but travelers are urged to be vigilant against criminal activity that targets non-Congolese, particularly in traffic jams and areas surrounding hotels, supermarkets, restaurants, and nightclubs. Outlying, remote areas are less secure because of high levels of criminal activity and the lack of adequate training, supervision, and salary for security forces. Individuals purporting to be security officials have detained and robbed U.S. citizens and other foreigners in Kinshasa. This type of crime occurs more frequently during the holiday season, including the Christmas and New Year's holidays and prior to the beginning of the school year.Vehicle thefts, burglaries, and armed robberies occur throughout the country with reports of some carjackings in the North Kivu area resulting in deaths. The Embassy recommends that motorists drive with doors locked and windows closed at all times. Do not permit soldiers or police officers to enter your vehicle, and avoid getting into the vehicle of anyone purporting to be a security official. Have color photocopies of your passport and other identity documents that you can give to security or police officials instead of the originals. If confronted, remain courteous and calm and, if threatened, do not resist. Please report any incident to the U.S. Embassy in Kinshasa.
Laws and regulations are not administered consistently in the DRC. Legal recourse in cases of theft and robbery is limited. Valuable items should be kept at home or in a secure location.
If you use public transportation or visit busy areas, be on guard against robbery and pick-pocketing, which are problems in all major cities in the DRC. The “sheggehs,” particularly in Kinshasa, can be aggressive and persistent.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in the DRC, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In the DRC, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you or if you take pictures of certain buildings. In some places, driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in the DRC, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It is very important to know what is legal and what is not wherever you go.While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Languages
Although French is the official language and is used in larger businesses and government, it is spoken by only about 10 percent of the population. Lingala is increasingly used as the national language. Regional languages are: Lingala, Kikongo, Tshiluba, and Swahili.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are severely limited, and medical materials are in short supply. It is wise to carry properly labeled prescription drugs and other medications; an adequate supply of prescription or over-the-counter drugs in local stores or pharmacies is generally not available. Payment for any medical services is expected in cash, in advance of treatment.Malaria is common throughout the DRC and malaria prophylaxis is strongly recommended. It is advisable to consult your primary care provider, prior to travel, concerning proper prophylaxis. Outbreaks of polio, cholera, typhoid, yellow fever, the Ebola virus, measles, influenza, and hemorrhagic fever also occur. Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in the DRC. Travelers are encouraged to obtain tuberculosis testing pre-travel and repeat 8-12 weeks after return. Travelers should take appropriate precautions to prevent the spread of HIV/AIDS.
Many insect-borne illnesses are present. Follow insect precautions at all times, including using insect repellant and mosquito nets when possible. A yellow fever vaccine is required for entry into the country. Travelers are encouraged to avoid contact with non-chlorinated fresh water to prevent schistosomiasis.
There is a high risk of traveler’s diarrhea and cholera throughout the country. This can be mitigated by using good judgment when choosing what food to eat and water to drink. When in restaurants, it is best to ask for bottled water and avoid ice.
Safety and Security
The Department of State’s Security Environmental Threat List Report has designated the DRC as a Critical Crime and High Political Violence Post. The security situation in many parts of the country remains fluid and problematic, including in Kinshasa. Visitors are encouraged to review the current Department of State Travel Warning for the DRC for additional details. Poor economic conditions, high unemployment, and low pay that is often in arrears for the military and police contribute to criminal activity in Kinshasa and throughout the country. Visitors are urged to remain vigilant at all times.Both inside and outside Kinshasa, security forces are known to set up occasional, spontaneous roadblocks, especially after dark. Vehicles are often searched for weapons and valuables, and passengers are checked for identity papers. Security forces regularly seek bribes. If confronted with such a situation, it is best to remain courteous and calm and remain inside your vehicle with doors locked. If detained, report the incident to the U.S. Embassy in Kinshasa as soon as possible.
The United Nations’ largest peacekeeping operation in the world operates in the DRC. Known by its French acronym of MONUSCO, it has nearly 18,000 peacekeepers deployed in the country, primarily in the east. Violence, nevertheless, persists in the eastern DRC due to the presence of numerous militias and armed groups, with sporadic outbreaks occurring in North Kivu, South Kivu, and northern Katanga provinces, as well as in the Ituri, Bas-Uele, and Haut-Uele Districts of Orientale province, and less frequently in Bas-Congo and Equateur provinces. Military actions against the Lord’s Resistance Army (LRA) in Haut Uele District have reduced the group’s presence but elements of the LRA are still active in this area and especially areas on the border with the Central African Republic and South Sudan. The DRC military has conducted a series of operations against the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda since January 2009. In April 2012, members of a former rebel group that had previously been integrated into the Congolese military mutinied resulting in heavy fighting in Masisi and Rutshuru territories as well as in Virunga National Park. In November 2012, these mutineers, known as M23, captured Goma, the capital of the province of North Kivu. Although they later withdrew from the city, they still occupy large portions of North Kivu and maintain a presence just kilometers from Goma. As a result, the number of internally displaced persons has risen to 1.7 million. Moreover, renewed violence among foreign and Congolese rebel groups present in the northern part of North Kivu and former Rwandan militants in the southern part of the province and throughout South Kivu pose a serious and significant risk to travelers in the region. This fighting underscores the persistent insecurity arising from the activities of rebel and other armed groups operating in the Kivus, which contribute to the overall high risks and dangers associated with travel to eastern Congo. The Department strongly recommends against all travel to the city of Goma and the province of North Kivu, and all but essential travel to the province of South Kivu and the Ituri region in the province of Oriental.
The security situation in the DRC remains unstable and difficult to predict. All travel by Embassy personnel outside of Kinshasa must be vetted by Embassy security staff for approval. Criteria considered in vetting such areas include, but are not limited to, political violence, criminal and violent activity, and the presence of armed or rebel groups. Travelers should take into consideration the above factors when making travel arrangements for the DRC.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in the DRC, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning the DRC is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Roads throughout the DRC are generally in poor condition, and often impassable in the rainy season. When driving in cities, keep windows up and doors locked. At roadblocks or checkpoints, documents should be shown through closed windows. In the event of an automobile accident, remain inside your vehicle and wait for police. If a hostile mob forms or you feel your life is in danger, leave the scene and proceed directly to the nearest police station or gendarmerie to report in the incident.
Official motorcades pose serious risks to drivers and pedestrians in Kinshasa. If you hear sirens or see security forces announcing the approach of a motorcade, pull off the road as far as possible and extinguish your headlights. Do not attempt to move until the entire motorcade has passed; security forces will indicate when this has occurred. Failure to comply may result in arrest or vehicle damage with possible personal injury.
Use of cell phones while driving is prohibited in the DRC. As with other traffic regulations, enforcement of this law is inconsistent. Distracted drivers pose a threat in large cities, especially Kinshasa.
Any form of public transportation is unregulated, generally unsafe, and unreliable. Taxis, mini-buses, buses, and trains are in poor mechanical condition and are often filled well beyond their intended capacity.
Drivers should stop their cars and pedestrians should stand still when passing a government installation during the raising and lowering of the Congolese flag. This ceremony occurs at roughly 7:30 a.m. and 6:00 p.m.