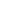Where is Canada located?
What countries border Canada?
Canada Weather
What is the current weather in Canada?
Canada Facts and Culture
What is Canada famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Despite close ties to the United States, Canadians emphasize they are not Americans living in a northern country. To be... More
- Family: Family life in Canada is as diverse as the country. In some areas, family size is small, and multigenerational families... More
- Personal Apperance: Some people think of Canada as a place where snow and cold weather are present year-round, which can severely restrict... More
- Recreation: Sports and recreation play a significant role in the social fabric of Canada. Popular national sports include Canadian football, basketball,... More
- Food and Recipes: Most Canadians eat three times a day. Breakfast can be a small meal of cereal, toast, yogurt, or some fruit.... More
- Visiting: When visiting a Canadian home or family, trust your instincts and remain open and friendly in their home. They will... More
Canada Facts
What is the capital of Canada?
| Capital | Ottawa |
| Government Type | federal parliamentary democracy (Parliament of Canada) under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm; federal and state authorities and responsibilities regulated in constitution |
| Currency | Canadian dollars (CAD) |
| Total Area |
3,855,081 Square Miles 9,984,670 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern North America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean on the east, North Pacific Ocean on the west, and the Arctic Ocean on the north, north of the conterminous US |
| Language | English (official) 58.8%, French (official) 21.6%, other 19.6% |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $46,200.00 (USD) |
Canada Demographics
What is the population of Canada?
| Ethnic Group - note | percentages add up to more than 100% because respondents were able to identify more than one ethnic origin |
| Ethnic Groups | Canadian 15.6%, English 14.7%, Scottish 12.1%, French 11%, Irish 12.1%, German 8.1%, Chinese 4.7%, Italian 4.3%, First Nations 1.7%, Indian 3.7%, Ukrainian 3.5%, Metis 1.5% |
| Languages | English (official) 87.1%, French (official) 29.1%, Chinese languages 4.2%, Spanish 3.2%, Punjabi 2.6%, Arabic 2.4%, Tagalog 2.3%, Italian 1.5% |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Canadian(s) adjective: Canadian |
| Population | 38,794,813 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.71% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 6.372 million Toronto, 4.308 million Montreal, 2.657 million Vancouver, 1.640 million Calgary, 1.544 million Edmonton, 1.437 million OTTAWA (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 81.9% of total population rate of urbanization: 0.95% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 19,234,729 female: 19,560,084 |
Canada Government
What type of government does Canada have?
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: minimum of 3 of last 5 years resident in Canada |
| National Holiday | Canada Day, 1 July (1867) |
| Constitution |
history: consists of unwritten and written acts, customs, judicial decisions, and traditions dating from 1763; the written part of the constitution consists of the Constitution Act of 29 March 1867, which created a federation of four provinces, and the Constitution Act of 17 April 1982 amendments: proposed by either house of Parliament or by the provincial legislative assemblies; there are 5 methods for passage though most require approval by both houses of Parliament, approval of at least two thirds of the provincial legislative assemblies and assent and formalization as a proclamation by the governor general in council; the most restrictive method is reserved for amendments affecting fundamental sections of the constitution, such as the office of the monarch or the governor general, and the constitutional amendment procedures, which require unanimous approval by both houses and by all the provincial assemblies, and assent of the governor general in council; amended 11 times, last in 2011 (Fair Representation Act, 2011) |
| Independence | 1 July 1867 (union of British North American colonies); 11 December 1931 (recognized by UK per Statute of Westminster) |
Canada Video
YouTube: Expoza Travel Canada Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Canada Geography
What environmental issues does Canada have?
| Overview |
The world's second-largest country in land area (3,851,809 square miles), Canada is bordered on the north by the Arctic Ocean, on the northeast by the Atlantic Ocean, on the south by the U.S., and on the west by the Pacific Ocean and Alaska. Much of Canada's industry is concentrated in the southeast near the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River, in an environment similar to adjacent areas of the U.S. To the northeast is the rolling Appalachian country of southern Quebec, the Maritime Provinces, and the Island of Newfoundland. Canada's most outstanding physical feature is the Shield, a rugged area of pre-Cambrian rock that surrounds Hudson Bay and covers most of eastern and central Canada--almost half the country. This semi-barren area and the Arctic Archipelago to the north are sparsely populated and, as yet, largely undeveloped. Another distinctive major region is the Canadian Prairie, an extension of the midcontinent Great Plains. This area lies between the western border of the Shield and the Canadian Rockies. It is the Canadian breadbasket and an area that is also rich in petroleum, gas, and other mineral resources. Far Western Canada, comprising most of British Columbia, is laced with towering mountain ranges. Most people there live on the temperate southwest coast and on Vancouver Island. |
| Climate | The climate varies greatly in the many diversified regions ranging from frigid to mild, but Canada generally may be described as lying in the cool Temperate Zone, with long, cold winters. |
| Border Countries | United States 8,893 km (includes 2,477 km with Alaska) |
| Environment - Current Issues | Air pollution and resulting acid rain severely affect lakes and damage forests; metal smelting, coal-burning utilities, and vehicle emissions impacting on agricultural and forest productivity; ocean waters are becoming contaminated due to agricultural, industrial, mining, and forestry activities |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Marine Life Conservation |
| Terrain | Mostly plains with mountains in the west and lowlands in the southeast |
Canada Economy
How big is the Canada economy?
| Economic Overview |
Canada resembles the US in its market-oriented economic system, the pattern of production, and high living standards. Since World War II, the impressive growth of the manufacturing, mining, and service sectors has transformed the nation from a largely rural economy into one primarily industrial and urban. Canada has a large oil and natural gas sector with the majority of crude oil production derived from oil sands in the western provinces, especially Alberta. Canada now ranks third in the world in proved oil reserves behind Venezuela and Saudi Arabia and is the world’s seventh-largest oil producer. The 1989 Canada-US Free Trade Agreement and the 1994 North American Free Trade Agreement (which includes Mexico) dramatically increased trade and economic integration between the US and Canada. Canada and the US enjoy the world’s most comprehensive bilateral trade and investment relationship, with goods and services trade totaling more than $680 billion in 2017, and two-way investment stocks of more than $800 billion. Over three-fourths of Canada’s merchandise exports are destined for the US each year. Canada is the largest foreign supplier of energy to the US, including oil, natural gas, and electric power, and a top source of US uranium imports. Given its abundant natural resources, highly skilled labor force, and modern capital stock, Canada enjoyed solid economic growth from 1993 through 2007. The global economic crisis of 2007-08 moved the Canadian economy into sharp recession by late 2008, and Ottawa posted its first fiscal deficit in 2009 after 12 years of surplus. Canada's major banks emerged from the financial crisis of 2008-09 among the strongest in the world, owing to the financial sector's tradition of conservative lending practices and strong capitalization. Canada’s economy posted strong growth in 2017 at 3%, but most analysts are projecting Canada’s economic growth will drop back closer to 2% in 2018. |
| Industries | Transportation equipment, chemicals, processed and unprocessed minerals, food products, wood and paper products, fish products, petroleum, natural gas |
| Currency Name and Code | Canadian dollars (CAD) |
| Export Partners | United States 76.7% |
| Import Partners | United States 53.1%, China 12.2%, Mexico 5.8% |
Canada News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Canada?
Source: Google News
Canada Travel Information
What makes Canada a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Canada is the second largest country in the world in land area and has large mountain ranges and extensive coastlines. Tourist facilities are widely available in much of the country, but the northern and wilderness areas are less developed and facilities there can be vast distances apart. It is a highly developed stable democracy with a vibrant economy. English and French are the official languages.
Crime
Although Canada generally has a lower crime rate than the United States, violent crimes do occur throughout the country, especially in urban areas. Visitors to large cities should be aware that parked cars are regularly targeted for opportunistic smash-and-grab thefts, and they are cautioned to avoid leaving any possessions unattended in a vehicle, even in the trunk. Due to the high incidence of such crimes, motorists in Montreal, Toronto, Vancouver, and some other jurisdictions can be fined for leaving their car doors unlocked or for leaving valuables in view.Auto theft in Montreal and Vancouver, including theft of motor homes and recreational vehicles, may even occur in patrolled and apparently secure parking lots and decks. SUVs appear to be particular targets of organized theft.
While Canadian gun control laws are much stricter than those in the United States, such laws have not prevented gun-related violence in certain areas.
Be aware of your surroundings. As in the United States, travelers in popular tourist areas may be targeted by pickpockets and other petty criminals.
In many countries around the world, counterfeit and pirated goods are widely available. Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, but if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While in a foreign country, a U.S. citizen is subject to that country's laws and regulations, which sometimes differ significantly from those in the United States, and may not afford the protections available to the individual under U.S. law. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating Canada’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs in Canada are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime, prosecutable in the United States.Canadian law prohibits the unlawful importation or trafficking of controlled substances and narcotics. Smugglers risk substantial fines, a permanent bar from Canada, and imprisonment.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Canada, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Importation of Firearms: Firearms are much more strictly controlled in Canada than in the United States. Violation of firearms restrictions may result in prosecution and imprisonment.
Visitors bringing any firearms into Canada, or planning to borrow and use firearms while in Canada, must declare the firearms in writing using a Non-Resident Firearm Declaration form. Visitors planning to borrow a firearm in Canada must obtain a Temporary Firearms Borrowing License in advance. These forms must be presented in triplicate and signed in front of a CBSA officer at the border (it is not possible to make photocopies at the border). Full details and downloadable forms are available at the Canadian Firearms Centre website, under the heading "Visitors / Non Residents."
Canadian law requires that officials confiscate any firearms and weapons from persons crossing the border who deny having the items in their possession. Confiscated firearms and weapons are never returned. Possession of an undeclared firearm may result in arrest and imprisonment. Travelers are strongly advised to inspect all belongings thoroughly prior to travel to Canada to avoid the accidental import of ammunition or firearms.
Canada has three classes of firearms: non-restricted, restricted, and prohibited.
Non-restricted firearms include most ordinary hunting rifles and shotguns.
These may be brought temporarily into Canada for sporting or hunting use during hunting season, use in competitions, in-transit movement through Canada, or personal protection against wildlife in remote areas of Canada.
Anyone wishing to bring hunting rifles into Canada must:
Be at least 18 years old;
Properly store the firearm for transport; and
Follow the declaration requirements described above.
Restricted firearms are primarily handguns; while they are not firearms, pepper spray, mace, and some knives also are included in this category.
A restricted firearm may be brought into Canada, but an Authorization to Transport permit must be obtained in advance from a Provincial or Territorial Chief Firearms Officer.
Prohibited firearms include fully automatic, converted automatics, and certain military-style weapons, including weapons designed for civilian use. A full list of prohibited weapons is available on the Canadian Firearms Centre website. Prohibited firearms are not allowed into Canada.
Pornography: Canada has strict laws concerning child pornography, and in recent years there has been an increase in random checks of electronic media of travelers entering Canada.
Computers and cell phones are subject to searches without a warrant at the border and illegal content can result in the seizure of the computer as well as detention, arrest, and prosecution of the bearer.
Possession of child pornography is punishable by up to 10 years in prison. Production and distribution of child pornography are punishable by up to 20 years in prison. Browsing for child pornography on the internet is punishable by up to 5 years in prison. Prohibitions cover visual representations of sexual activity by persons (real or imaginary) under the age of 18 and include comic book imagery such as anime and manga.
Alcohol-related driving offenses, such as driving while intoxicated (DWI), driving while ability-impaired, and driving under the influence (DUI) of alcohol, are criminal offenses in Canada. Penalties are heavy, and any prior conviction (no matter how old or how minor the infraction) is grounds for exclusion from Canada. U.S. citizens with a DWI record must seek approval for rehabilitation from Canadian authorities before traveling to Canada, which requires several weeks or months to process.
Languages
English (official) 87.1%, French (official) 29.1%, Chinese languages 4.2%, Spanish 3.2%, Punjabi 2.6%, Arabic 2.4%, Tagalog 2.3%, Italian 1.5%
Medical Facilities and Health Information
The level of public health and sanitation in Canada is high. Canada’s medical care is of a high standard but is government-controlled. Quick and easy access to ongoing medical care is difficult for temporary visitors who are not members of each province’s government-run health care plans. Many physicians will not take new patients. Access to a specialist is only by referral and may take months to obtain. Emergency room waits can be very long. Some health care professionals in the province of Quebec may speak only French.Traveler’s medical insurance is highly recommended even for brief visits. No Canadian health care provider accepts U.S. domestic health insurance, and Medicare coverage does not extend outside the United States. Visitors who seek any medical attention in Canada should be prepared to pay cash in full at the time the service is rendered.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Canada, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Canada is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance. As in the United States, all emergency assistance in Canada can be reached by dialing 911.Transport Canada is the Canadian federal government agency responsible for road safety, although each province or territory has the authority to establish its own traffic and safety laws and issue driving licenses. For detailed information on road conditions throughout Canada, as well as links to provincial government websites, please see the Transport Canada website or the Canadian Automobile Association (CAA) website. The CAA honors American Automobile Association membership. Some automobile warranties of vehicles purchased in the United States may be invalid in Canada; please check the warranty of your vehicle.
Driving in Canada is similar to driving in many parts of the United States. Distances and speeds, however, are posted in kilometers per hour and some signs, particularly in Quebec, may only be in French. U.S. driver’s licenses are valid for visitors in Canada. Proof of auto insurance is required. U.S. auto insurance is accepted as long as an individual is a tourist in Canada. U.S. insurance firms will issue a Canadian insurance card, which should be obtained and carried prior to driving into Canada. For specific information concerning Canadian driving permits, mandatory insurance, and entry regulations, please contact the Canadian National Tourist Organization.
Unless otherwise posted, the maximum speed limit in Canada is 50km/hr (32 miles/hr) in cities and 80km/hr (50 miles/hr) on highways. On rural highways, the posted speed limit may be 100km/hr (approximately 60 miles/hr). Seat belt use is mandatory for all passengers, and child car seats must be used by children under 40 pounds.
Some provinces require drivers to keep their vehicles’ headlights on during the day and some have banned driving while using a hand-held cell phone. Motorcycles cannot share a lane, and safety helmets for motorcycle riders and passengers are mandatory.
Many highways do not have merge lanes for entering traffic. Emergency vehicles frequently enter the oncoming traffic lane to avoid congestion. Drivers should be aware that running a red light is a serious concern throughout Canada and motorists are advised to pause before proceeding when a light turns green. Turning right at a red light is prohibited on the Island of Montreal, and motorists are subject to substantial fines.
It is illegal to take automobile radar detectors into Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, the Yukon, or the Northwest Territories, regardless of whether they are used or not. Police there may confiscate radar detectors, operational or not, and impose substantial fines.
Winter travel can be dangerous due to heavy snowfalls and hazardous icy conditions. Some roads and bridges are subject to periodic winter closures. Snow tires are required in some provinces. The CAA has tips for winter driving in Canada. Travelers also should be cautious of deer, elk, and moose while driving at night in rural areas.
Highway 401 from Detroit to Montreal, which is one of the busiest highways in North America, has been the scene of numerous deadly traffic accidents due to sudden, severe, and unpredictable weather changes, high rates of speed, and heavy truck traffic.
There have been numerous incidents on Canadian highways involving road racing and dangerous truck driving. Drivers can be aggressive, exceeding speed limits and passing on both sides, and police enforcement is spotty. In addition, approaches to border crossings into the United States may experience unexpected traffic backups. Drivers should be alert, as lane restrictions at border approaches exist for drivers in NEXUS and FAST expedited inspection programs.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe